How to Run Scenarios in AVERT
The AVERT Overview and Step-by-Step instructions provide an overview of how AVERT works, and step-by-step demonstrations of how to use AVERT.
Available Regions for AVERT Analysis
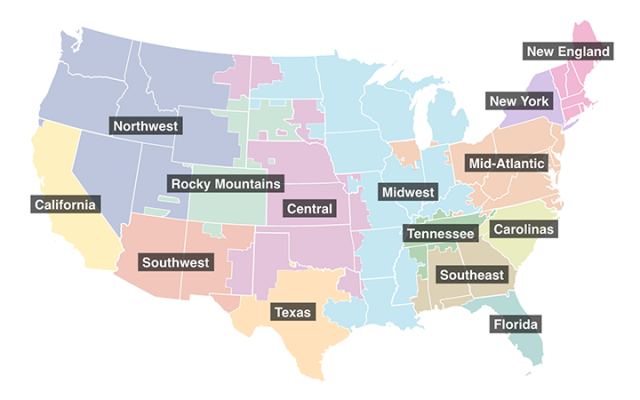
Note: AVERT does not currently model emissions scenarios for Alaska or Hawaii.
Two versions of the AVERT Main Module are available: a fully-featured Excel version and a streamlined web-based tool. The online tool provides similar functionality to the downloadable Excel tool, without the need to download any files or software. The online version relies on the most recent year of input data, creates commonly used output formats, and allows users to save results. It also can perform analyses for a selected state, including states that span more than one AVERT region. Some users will find that the Web Edition meets their needs, while others may prefer using the Excel version to access different data years, custom load profiles, future scenarios, and additional outputs.
AVERT’s Main Module estimates the changes in emissions likely to result from energy programs, policies, and projects in reference to a base-year or future-year scenario. Installation of AVERT’s Statistical Module and AVERT’s Future-Year Scenario Template is not necessary to use AVERT’s Main Module to estimate emissions impacts modeled in a historical base year. However, modeling emissions impacts with reference to user-created future years requires all three AVERT modules.
Users select one of 14 AVERT regions for analysis, upload one regional data file, and input data on the type of program they want to analyze in AVERT. For energy efficiency policies and programs, users should have annual savings impacts (MWh or MW) and an understanding of the policies’ or programs’ temporal profiles (e.g., would the program save energy during peak periods or the same amount through the year). For renewable energy programs, users will need to know the total capacity of the solar or wind resource they are interested in analyzing. For electric vehicle policies and programs, users will need to know the number of vehicles by types and the location of deployment. For energy storage resources, users will need to know the energy storage capacity, duration, and charging pattern and whether to pair the storage with solar generation.
Users will then run the model to calculate the changes in generation and emissions from the chosen scenario. The Excel-based calculation can take up to 10 minutes depending upon the region and computer capabilities.
The AVERT Main Module provides output in the form of county-level emissions and generation tables and charts for the user’s selected AVERT region. It also produces SMOKE-formatted data for advanced air modeling applications, as well as data that can be used with EPA’s COBRA tool to quantify and monetize public health impacts.
