Domestic Action Plans (DAPs)
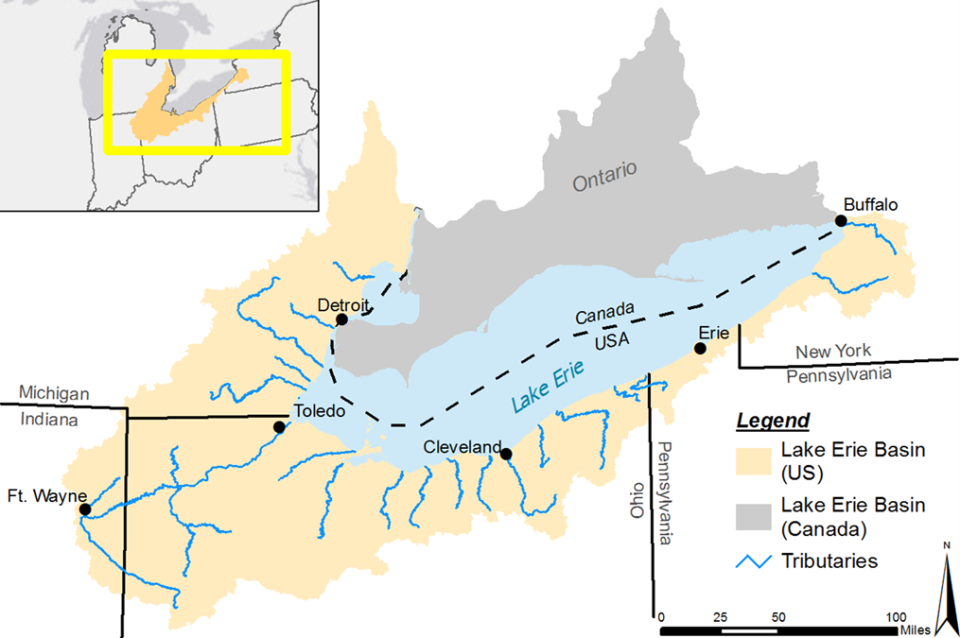
Domestic Action Plans are the “road maps” for phosphorus control efforts being undertaken by states, the province of Ontario, and the U.S. and Canadian governments. Each jurisdiction engaged stakeholders in the development of their domestic action plans in 2017, before finalizing in 2018. There are six DAPs in total: one for Canada-Ontario; one for the U.S.; and four specific state-level plans for Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, and Pennsylvania. Note that New York state is not obligated to produce a stand-alone DAP because there are no phosphorus targets for the eastern basin of Lake Erie. However, New York is an active participant in the GLWQA Nutrients Annex Subcommittee and their efforts are captured in the U.S. Action Plan.
In the U.S., reducing phosphorus loads by 40 percent will be challenging to achieve because:
- The magnitude of reduction is very large – over 7 million pounds annually.
- The contributing area is also very large. (There are more than 4 million acres of cropland in the Maumee River watershed alone).
- The majority of phosphorus is from nonpoint sources.
- Excess phosphorus has accumulated in fields and waterways over many years, due to fertilizer application and soil erosion.
