Technical Assistance
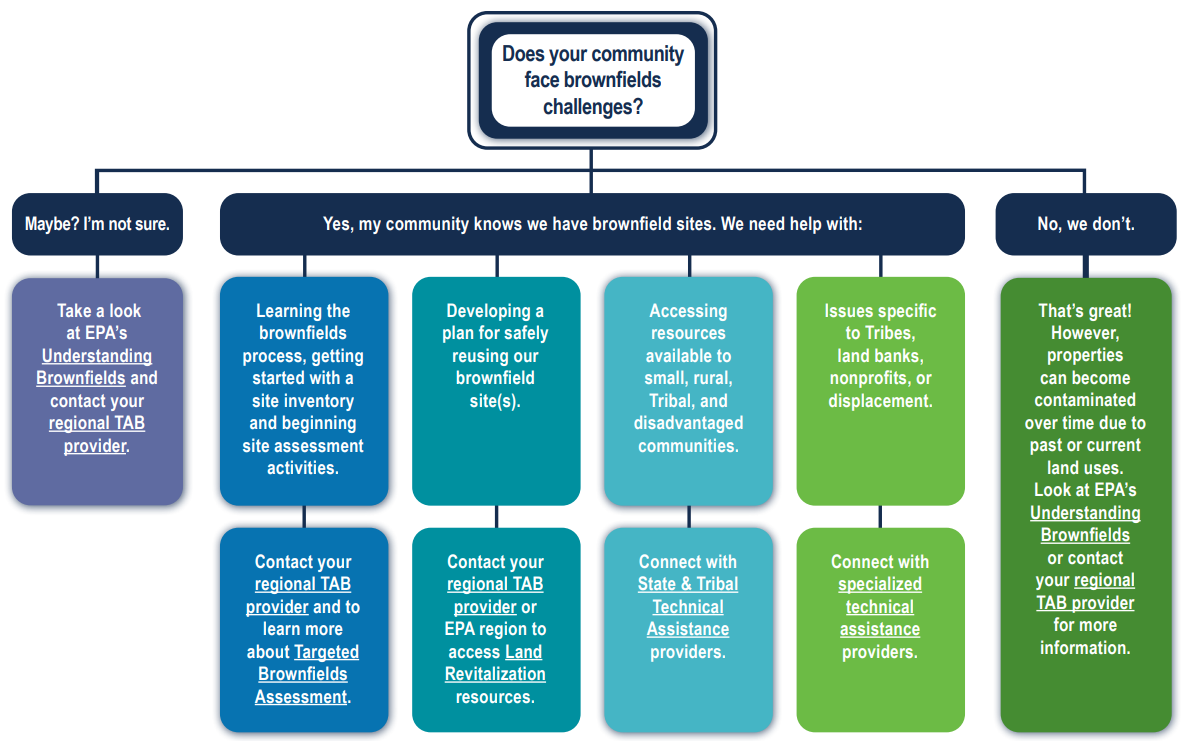
Does your community face brownfields challenges? (pdf)
EPA provides several types of free technical assistance to support local efforts to address brownfield sites:
- Technical Assistance to Brownfields Communities (TAB) Program – EPA funds regionally based expert organizations to support communities in each of its 10 EPA regions and nationwide.
- Nationwide Brownfields Technical Assistance Providers – EPA funds nationwide providers to assist communities with brownfields issues.
- Targeted Brownfields Assessment – EPA contractors assist communities with site assessments and planning.
- Land Revitalization Technical Assistance - EPA contractors assist communities with brownfields reuse planning activities.
- CERCLA Section 128(a) Technical Assistance Grants ("TAG") - EPA funds TAG to Section 128(a) cooperative agreement recipients. The funding must benefit small communities, Indian Tribes, rural areas or disadvantaged areas.
Also see these additional resources available to assist organizations with their brownfields projects.
Technical Assistance to Brownfields Communities
The Technical Assistance to Brownfields Communities (pdf) provides technical assistance to communities, states, Tribal Nations and other public entities to help address their brownfield sites and to increase their understanding and involvement in brownfields cleanup, revitalization and reuse. The program supplements other efforts under the Brownfields Program.
TAB is available at no cost to communities. EPA funds regionally based expert organizations to support communities in each of its 10 regions. TAB grant recipients, also known as TAB providers, serve as an independent resource and can provide expert technical assistance and guidance to help communities, among other things, understand how to:
- Prepare brownfields grant applications.
- Perform site inventories.
- Review historical information.
- Design site investigations, sampling and field analysis.
- Plan cleanup and redevelopment.
How to Access
Any community with a brownfields concern can reach out to their regional TAB provider for assistance. For general inquiries, contact a brownfields representative in your EPA regional office.
EPA Region 1
EPA Region 2
EPA Region 3
EPA Region 4
- International City/County Management Association
- New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) TAB Program
EPA Regions 5, 6, 7 and 8
EPA Regions 9 and 10
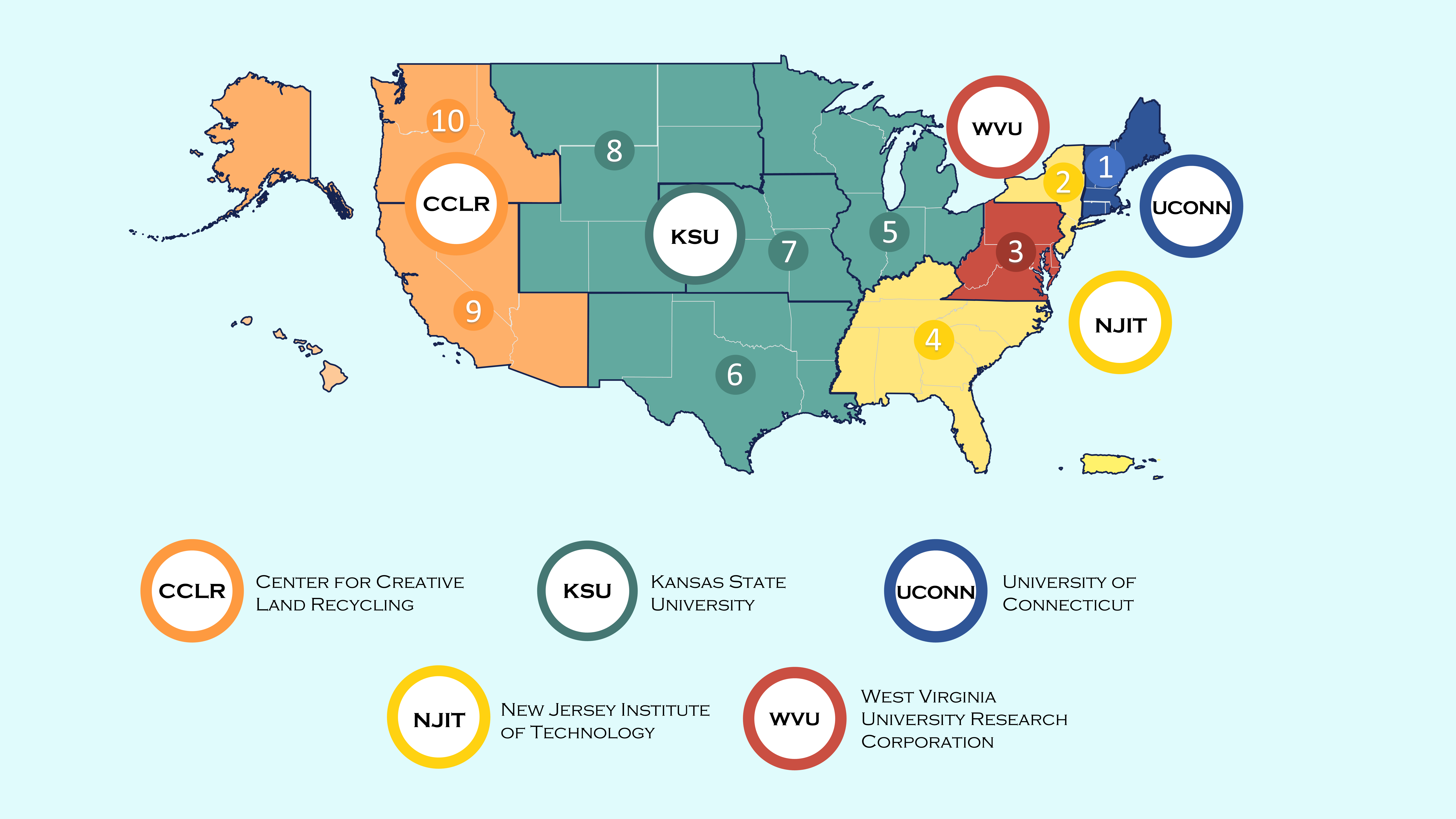
Nationwide Brownfields Technical Assistance Providers
EPA funds a variety of nationwide expert organizations to assist communities with brownfields issues. Technical assistance is available at no cost to communities. Providers include:
- Technical Assistance to Tribes – Kansas State University provides technical assistance to Tribes across the country including assistance to Brownfields Job Training recipients and entities seeking to establish a Brownfields Job Training Program.
- Technical Assistance for Nonprofits (through September 2028) – Groundwork USA provides technical assistance to nonprofits across the country seeking assistance with brownfield revitalization projects. Technical assistance provided is centered in equitable development strategies and principles for reuse. Learn more about Groundwork USA's Nonprofit Technical Assistance.
- Brownfields Land Banking Strategies (through 2027) – The Center for Community Progress (Community Progress) is developing materials to support communities who are interested in using land banking strategies to address brownfield sites. Reach out to Community Progress if you need assistance connecting with land banks, understanding the use of land banks in brownfields projects, or if you are a land bank leader interested in supporting brownfield remediation. Visit Community Progress's website and sign up to receive their newsletter.
- National Brownfields Training Conference (through 2030) – ICMA hosts the National Brownfields Training Conference. The National Brownfields Training Conference brings together stakeholders from government, industry, and communities to share knowledge and best practices on the remediation and redevelopment of brownfields. The conference features a range of sessions, workshops, and networking events that cover topics such as financing, liability, environmental justice, and community engagement, with the goal of promoting the sustainable cleanup and revitalization of contaminated sites across the United States.
- Brownfields Revitalization Anti-Displacement Strategies Program (through 2027) - UMass Dartmouth, in collaboration with the University of Louisville and Florida State University, provides guidance and training in developing and applying equity-centered and economically inclusive anti-displacement strategies to communities looking for assistance to address displacement and gentrification as part of their redevelopment.
- Technical Assistance to Brownfields Job Training (through March 2025) - Tetra Tech, in collaboration with Adaapta, provides technical assistance across the country provides technical assistance across the country to existing and potential Brownfields Job Training Grant recipients. If you need assistance related to Brownfields Job Training, please complete this inquiry form.
- Brownfields Revolving Loan Fund Technical Assistance (through 2029) - Grow America, in collaboration with the International City/County Management Association, provides technical assistance across the country to existing and potential Brownfields Revolving Loan Fund Grant recipients. Reach out to Grow America if you need assistance related to the Brownfields Revolving Loan Fund Program.
How to Access
Communities may reach out directly to the organizations above for free brownfields technical assistance.
Learn More
- This EPA webinar highlights the range of assistance available to brownfields communities at no cost.
- For more information, contact a brownfields representative in your EPA regional office.
Targeted Brownfields Assessment
EPA’s Targeted Brownfields Assessment (TBA) program helps communities understand potential contamination at a brownfield site and plan for cleanup and redevelopment. The program supplements other efforts under the Brownfields Program and provides assistance at no cost to communities. An EPA contractor delivers TBA assistance on behalf of an eligible entity. Services include the following:
- Site assessments
- Cleanup options and cost estimates
- Community outreach on future uses and redevelopment plans
Specific activities may include the following:
- An American Society for Testing and Materials Phase I Environmental Site Assessment, which includes a background and historical investigation and site inspection
- A full site assessment, including sampling activities to identify types and concentrations of contaminants and the areas of contamination that must be cleaned up
- Determining how much more investigation is needed and/or establishing cleanup options and cost estimates based on future uses and redevelopment plans
The TBA Program works closely with your state environmental agency. Our goal is a "seamless" transition into your state's program, if necessary. TBAs are not grants but rather a service that EPA provides at no cost to the requestor. TBAs are provided under the direction of the EPA regional TBA coordinator(s) and are conducted by environmental consultants currently under contract with EPA. The cost of these assessments range between $50,000-$100,000. It is also important to note that this program does not provide assistance to conduct site cleanup or building demolition activities.
TBA Coordinators by Region
| Region | TBA Coordinator(s) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Katy Deng |
| 2 | Yocasta DeJesus |
| 3 | Christian Smith |
| 4 | David Hayes |
| 5 | Melanie Sorman (cc John Jurevis) |
| 6 | Mike Kennedy and Roxanne Welch (cc Althea Foster) |
| 7 | Lisa Dunning and Sandeep Mehta |
| 8 | Christina Wilson and Joann Jeplawy |
| 9 | Scott Stollman and Dominic Maccormack |
| 10 | Molly Vaughan (cc Terri Griffith) |
Eligibility
EPA offers TBA to public entities (e.g., municipalities, regional planning commissions) and nonprofit organizations that already have redevelopment plans for a contaminated property. They can apply on behalf of a specific site they currently own or can become owners through other means (e.g., tax foreclosure).
Sites not owned by applicants may be eligible if they are abandoned: the site owner has shown no interest in the property, has not paid taxes on the property and does not have the resources for the required site assessment.
Private parties are not eligible for assistance in assessing and cleaning up sites for redevelopment.
How to Access
TBA is available directly through EPA regional offices or from State and Tribal Voluntary Response Program offices receiving funding. Sites are selected on a rolling basis.
Contact a brownfields representative in your EPA regional office to learn more.
What Factors Help Ensure a Successful Application?
Site Control and Ownership Transfer is Not an Impediment
- Site is publicly owned either by municipality or through a quasi-public entity such as a redevelopment authority or industrial development corporation.
- Site is owned by a nonprofit entity such as a community development corporation.
- Site is privately owned, and a clear means of recouping EPA expenditures is available (e.g., through an agreement with the owner or developer or through a lien), or the private entity has performed prior environmental work at the site.
There is Strong Municipal Commitment
- There is a strong municipal commitment as demonstrated by a willingness to legally take the property if necessary, establishment of financial incentives, or commitment of municipal resources for other components of the project.
There is Clear Municipal/Community Support for the Property's Revitalization
- The site is clearly an integral part of a local development plan and there is no known public opposition.
There are Adequate Resources and High Developer Interest
- The municipality or potential site developer has demonstrated an ability to leverage additional funds for cleanup and other future work at the site; and/or the site has strong development potential as demonstrated by past or present interest by a developer(s).
EPA Assessment Assistance is Crucial
- Lack of site assessment is the major obstacle to redevelopment and other resources are not available for assessing the site.
There is State/Congressional Support
- The state/congressional members have no objection to federal involvement or the redevelopment project.
Existing Information Supports Directing Resources to the Site
- Based on existing information, the site is likely to have low to moderate levels of contamination.
- Commitments are in place for the cleanup and redevelopment of the site.
- Redevelopment will result in benefits to the community, such as an increase in jobs for the surrounding residents.
Project Area has a Clear Need for Revitalization
- The project has significant deterioration or significant environmental justice issues, which provide a clear need for revitalization.
There is State Support
- There is clear coordination between EPA and the state program.
Project is Consistent with other Economic Redevelopment Initiatives
- Site has an important linkage to other EPA/state initiatives.
- A direct health/environmental threat will be mitigated, or site revitalization will serve to spur further beneficial activity in nearby locations.
- There is consistency with other federal agency Brownfields efforts, e.g., economic redevelopment efforts.
Land Revitalization Technical Assistance
EPA's Land Revitalization Technical Assistance (LR TA) can help a community determine which types of brownfield site reuses are feasible, given local conditions (e.g., economic, infrastructure, social, climate and environmental site conditions), infrastructure availability, community site design preferences, and funding or financing resources. Understanding the community's goals for site reuse is an important part of making local decisions around how to assess, remediate and safely reuse the brownfield.
LR TA typically supplements brownfields grants and other technical assistance provided under the Brownfields Program. An EPA contractor delivers the LR TA support at no cost to communities.
LR TA can help a community navigate many of the site reuse challenges posed by brownfield sites. While land revitalization looks different in every community, many brownfields reuse planning activities can be supported through LR TA, including:
- Information gathering on brownfield site and local conditions
- Conceptual design
- Understanding implementation resources
How to Access
As resources allow, EPA's Regional Brownfields and Land Revitalization Programs can connect communities with LR TA support. Individuals and private, for-profit organizations are not eligible to receive LR TA.
Contact a brownfields or land revitalization representative in your EPA regional office to learn more.
CERCLA Section 128(a) Technical Assistance Grants ("TAG")
Section 128(a) TAG is provided to Section 128(a) cooperative agreement recipients so that they may provide technical assistance to small communities, Indian Tribes, rural areas or disadvantaged areas. By law, the maximum amount per Section 128(a) TAG is $20,000.
Uses for these funds include providing training, research, and technical assistance to facilitate the inventory of brownfield sites, site assessments, remediation of brownfield sites, community involvement or site preparation. See the Section 128(a) Technical Assistance Grant ("TAG") Fact Sheet (pdf) for more information.
Eligibility
Eligible entities for Section 128(a) TAG funding include:
- A State, as defined in CERCLA § 101(27)
- An Indian tribe, as defined in the Federal Register Notice at 67 FR 67181, Nov. 4, 2002
The request must be on behalf of a(n):
- Small community
- Indian tribe
- Rural area
- Disadvantaged area
Multiple eligible communities may be assisted in one grant.
How to Access
Section 128(a) TAG is awarded as part of the annual CERCLA 128(a) State and Tribal Response program funding cycle. Appendix A of the annual grant funding guidance provides the specific instructions for requesting 128(a) TAG funds in a given fiscal year. Copies of the guidance can be obtained from EPA's State and Tribal Response Program Grants webpage. Requests must include the information listed in Appendix A of the guidance and be submitted to the appropriate Regional EPA Brownfields office by the stated deadline.
Additional Resources
Brownfields Road Map to Understanding Options for Site Investigation and Cleanup
Brownfields Grant Recipients' Road Map to Understanding Quality Assurance Project Plans (pdf) explains how to assess and clean up a brownfields site, including:
- Setting reuse goals and planning.
- Understanding regulations and liability concerns.
- Engaging the community.
- Identifying funding sources.
Brownfields Grant Recipients’ Road Map to Understanding Quality Assurance Project Plans
Brownfields Grant Recipients' Road Map to Understanding Quality Assurance Project Plans (pdf) helps EPA Brownfields Assessment Grant recipients design and complete site assessments more efficiently and effectively through quality assurance practices.
Hazardous Waste Cleanup Information
The Contaminated Site Clean-Up Information (CLU-IN) Web Site provides information about hazardous waste remediation.
EPA-Recommended Mapping Tools
EPA has developed and identified a range of mapping and spatial tools that may be helpful to communities as they pursue land revitalization goals.
